What is Barcode Read Rate and Why it is Important?

Key Takeaways
- Definition: Barcode read rate is the percentage of barcodes successfully scanned on the first attempt
- Business Impact: Low read rates cause production delays, increased costs, and data gaps
- Ideal Target: Manufacturing operations should aim for 99%+ read rates
- Technology Difference: Image-based readers typically achieve higher read rates than laser scanners
- ROI Factor: Improving read rates directly enhances production throughput and efficiency
Understanding Barcode Read Rates
In manufacturing environments, barcodes serve as the critical link between physical products and digital tracking systems. They enable manufacturers to track parts as they move through production, from individual components to assemblies, sub-assemblies, and finally to finished products ready for distribution.
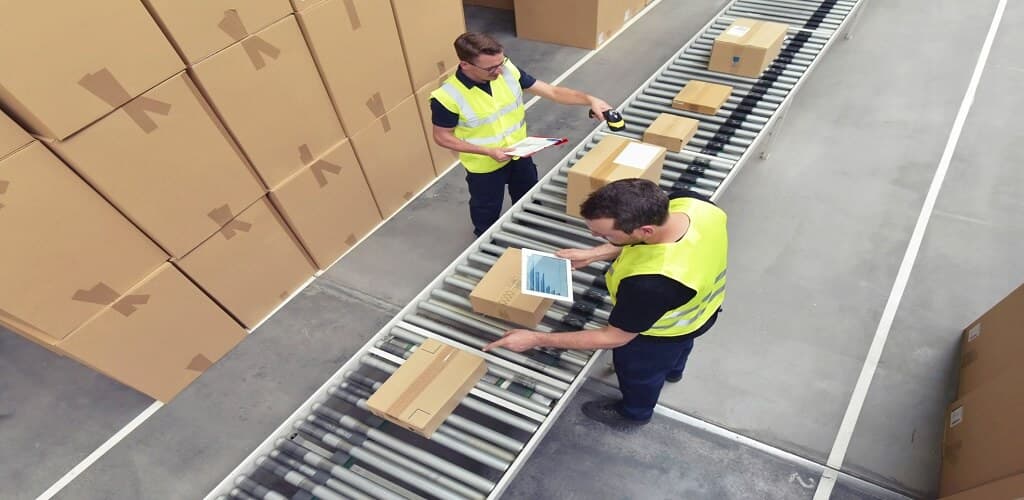
 Image-based barcode readers can achieve higher read rates than traditional laser scanners
Image-based barcode readers can achieve higher read rates than traditional laser scanners
The barcode read rate—the percentage of barcodes successfully read by a scanner on the first attempt—is a fundamental metric for measuring the effectiveness of this tracking system. While a perfect 100% read rate is the theoretical ideal, manufacturing operations typically target 99% or higher to maintain efficient production flow.
Why Read Rates Matter
The importance of high barcode read rates extends far beyond simple data collection:
1. Production Efficiency
Each "no-read" event (when a barcode cannot be scanned successfully) typically requires intervention:
- Production may pause while an operator manually enters data
- Products might be diverted to a secondary inspection station
- Items may need to be rescanned, creating bottlenecks
These interruptions directly impact production throughput and efficiency. A manufacturing line running at 120 parts per minute with a 95% read rate effectively loses the capacity to process 6 parts every minute due to scanning failures.
2. Data Integrity
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) rely on complete, accurate data to:
- Track production progress
- Manage inventory
- Ensure quality control
- Enable product traceability
When barcodes fail to read, this creates gaps in the data that can compromise these critical functions. In regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or automotive manufacturing, these data gaps can create compliance issues and liability concerns.
3. Cost Implications
The financial impact of poor read rates includes:
- Direct Labor Costs: Personnel required to handle exceptions
- Lost Production Time: Reduced throughput and capacity
- Rework Expenses: Correcting issues with unreadable codes
- Shipping Delays: Problems identifying or sorting products
- Customer Penalties: Chargebacks for non-compliant or unreadable codes
4. Process Reliability Indicator
Read rates serve as a key performance indicator for overall process health:
- Declining read rates often signal upstream problems with printing or marking equipment
- Variations in read rates between production lines can highlight inconsistent processes
- Patterns in read rate failures can identify specific product or material issues
Common Challenges Affecting Read Rates
Several factors can negatively impact barcode read rates in manufacturing environments:
1. Print or Mark Inconsistency
- Faded or smudged printing
- Inconsistent mark depth in direct part marking
- Variations in contrast or reflectivity
- Printer maintenance issues
2. Improper Reading Position
- Incorrect scanner placement relative to the barcode
- Variable product positioning on the conveyor
- Inconsistent barcode placement on products
- Curved or irregular surfaces affecting scan angle
3. Low Contrast
- Insufficient difference between dark and light elements
- Background colors interfering with readability
- Reflective packaging or surfaces
- Poor lighting conditions
4. Environmental Factors
- Dust or debris obscuring codes
- Vibration affecting scanner performance
- Extreme temperatures affecting printing quality
- Moisture or condensation on products
Image-Based Solutions for Improved Read Rates
Traditional laser-based barcode scanners have significant limitations that affect read rates:
- They require precise alignment with the barcode
- They struggle with damaged or poorly printed codes
- They typically read only in one direction
- They cannot read 2D codes like QR codes or Data Matrix
Modern image-based barcode reading solutions address these limitations through advanced technology:
Key Advantages:
- Omnidirectional Reading: Can read barcodes in any orientation
- Code Reconstruction: Can piece together partially damaged codes
- Multiple Code Types: Support for 1D, 2D, and direct part marking
- Greater Depth of Field: Can read codes at varying distances
- Image Capture: Stores images of failed reads for analysis
- Advanced Algorithms: Uses machine learning to improve performance
These capabilities enable image-based readers to achieve significantly higher read rates in challenging manufacturing environments, often approaching the ideal 100% even with variable code quality and positioning.
Implementation Considerations
When implementing or upgrading barcode reading systems to improve read rates, manufacturers should consider:
1. Application Assessment
- Barcode types and sizes in use
- Production line speeds
- Environmental conditions
- Mounting constraints
2. Technology Selection
- Image-based vs. laser technology
- Fixed-mount vs. handheld readers
- Resolution requirements
- Lighting options
3. Integration Requirements
- Communication protocols
- Trigger mechanisms
- Rejection systems for no-reads
- Data management
4. Performance Monitoring
- Read rate tracking systems
- Image storage for failed reads
- Regular performance reviews
- Continuous improvement processes
Return on Investment
Investing in high-performance barcode reading solutions typically delivers rapid ROI through:
- Increased Throughput: More products processed per hour
- Reduced Labor: Less manual intervention required
- Fewer Errors: Improved data accuracy
- Better Traceability: Complete product history
- Process Insights: Data for continuous improvement
For a typical manufacturing operation, improving read rates from 95% to 99% can increase effective production capacity by 4% without any other process changes—often paying for the technology investment within months.
Conclusion
Barcode read rates serve as a critical performance metric in manufacturing environments, directly impacting production efficiency, data integrity, and operational costs. While achieving perfect 100% read rates remains challenging, modern image-based barcode reading solutions can consistently deliver the 99%+ performance needed for efficient operations.
By understanding the factors that affect read rates and implementing appropriate technology solutions, manufacturers can significantly improve this key metric, enhancing both productivity and profitability. For operations struggling with barcode reading challenges, upgrading to image-based solutions offers a proven path to higher read rates and more reliable production tracking.
This article provides a historical perspective on barcode reading technology. While Visionify now specializes in computer vision solutions for various industries, we recognize the continuing importance of reliable barcode reading in manufacturing environments.
Want to learn more?
Discover how our Vision AI safety solutions can transform your workplace safety.
Schedule a DemoSchedule a Meeting
Book a personalized demo with our product specialists to see how our AI safety solutions can work for your business.
Choose a convenient time
Select from available slots in your timezone
30-minute consultation
Brief but comprehensive overview of our solutions
Meet our product experts
Get answers to your specific questions
Related Articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest safety insights and updates delivered to your inbox.


